![]()
Quality monitoring allows you to observe an agent’s phone calls, email and web chats, and score those interactions against an agreed–upon definition of great customer interaction.
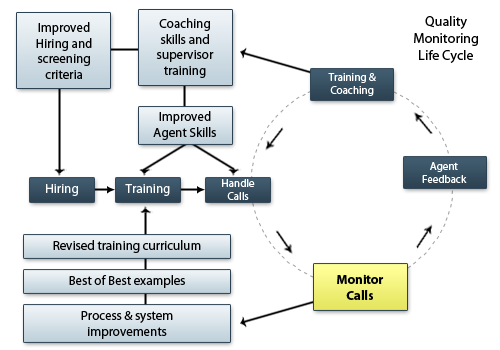
The quality monitoring lifecycle is about process improvement and involves the following steps:
- The lifecycle begins during hiring and training, when a prospective agent’s performance is monitored and evaluated to identify weaknesses and skills gaps.
- After training is successfully completed, the agent begins handling customer interactions and is monitored regularly to identify issues and performance gaps. Distinguish between deficient agent performance and deficiencies in the elements being evaluated or in the service process.
- Evaluate agent performance against established standards and for any performance that merits action, note, record, and refer to the responsible component (HR, QA, Training, etc.). Ensure the agent gets both positive and negative feedback to improve their performance. Provide ongoing training and coaching. Repeat this process continuously throughout the agent’s tenure.
- Process and system improvement issues, as well as needed training curriculum revisions, are often identified through monitoring sessions. These issues are fed back to the responsible component for action.
Traditional quality monitoring involves reviewing a random sample of interactions, assessing them for general quality standards, and then generating monthly reports based on average scores. Most contact centers only evaluate a very small percentage of their calls this way. Quality monitoring tools will increase the efficiency of these evaluation processes by reducing the administrative effort in recording agent interactions by storing, analyzing, and scoring the interactions for quality.
Some quality monitoring solutions combine call–recording functionality with performance management, speech analytics and e–learning capabilities to address skills gaps. These tools help formalize and add substance to quality transactions and make the quality–monitoring process more efficient and effective.
Importance of Monitoring Agents
Quality is the cornerstone of any business. Contact centers are no different. Quality monitoring affects all aspects of operation, from hiring and training agents, to honing superior agent skills and even discovering and correcting process problems. Monitoring identifies process and performance deficiencies so that corrective actions can be taken in a timely manner, and affords ongoing opportunities to make continual, incremental improvements.
It remains one of the most critical factors in developing a high–performance workforce, by maintaining operational efficiency and delivering superior customer service. In order for a contact center to function effectively and achieve high–performance status, an organization must establish a strong quality–monitoring program and devote sufficient resources to ensure its continued success.
Implementation of Quality Monitoring?
Effective quality–monitoring program generally involves the following steps:
- Identifying the key performance criteria that result in successful interactions.
- Selecting and defining measurable attributes that support each of the criteria.
- Determining the weight for each criterion in the total call score.
- Selecting the scoring method for each criterion and creating a uniform monitoring form that will be used by all.
- Defining the monitoring process and performance benchmarks.
- Training all contact center members (both quality monitors and agents) about the performance criteria and benchmarks.
- Conducting trial monitoring sessions to work out any bugs before you begin live monitoring.
- Recording results of the monitoring sessions and producing reports showing performance trends by individual agent and the whole team.
- Integrating calibration into the quality monitoring process.
When should you monitor?
When you actually perform monitoring will depend on a number of variables. Variables that will affect the monitoring schedule include:
- Peak hours of the day
- Peak days of the week
- Peak week of the month
- Agent group being monitored (new hires vs. veteran agents) & Monitor’s schedule
Quality Monitoring Solutions:
The following functions are provided to supervisors/trainers:
- Selective recording of calls (voice and screen) according to a variety of user-defined or project-specific parameters
- Easy and comfortable search for calls according to user-definable criteria (agent, content, time of day, CTI event)
- Highly flexible generation and use of evaluation templates
- Easy creation and distribution of management reports
- Conversion of calls into instructive examples using additional functions (eCoaching)
- Integration of agents as active parts into the Quality Monitoring process
- eLearning and eCoaching capabilities to close the loop between recording and evaluation of agents
Typical Quality Monitoring Task
- Definition of evaluation templates
- Initiating measures for quality evaluation
- Evaluating the quality
- Interpretation of the individual evaluations
- Definition of training package templates
- Allocation and administration of training package templates
- Consolidated analysis of quality measures
- Targeted planning of speech analytics
Benefits of Quality Monitoring
Customers:
- Improve customer service
- Personalized relationships
- Reduce Hold Times and Transfers
Agents:
- Effective training and coaching
- Improved job Skills
- Increased Motivation
Supervision
- Effective management
- Sensitivity to service quality
- Transparent communications
Companies:
- Increased loyalty
- Reduce employee turnover
- Improve productivity
- Continuous improvement process
- Reduce training costs
Quality monitoring Life Cycles
 LOGIN
LOGIN